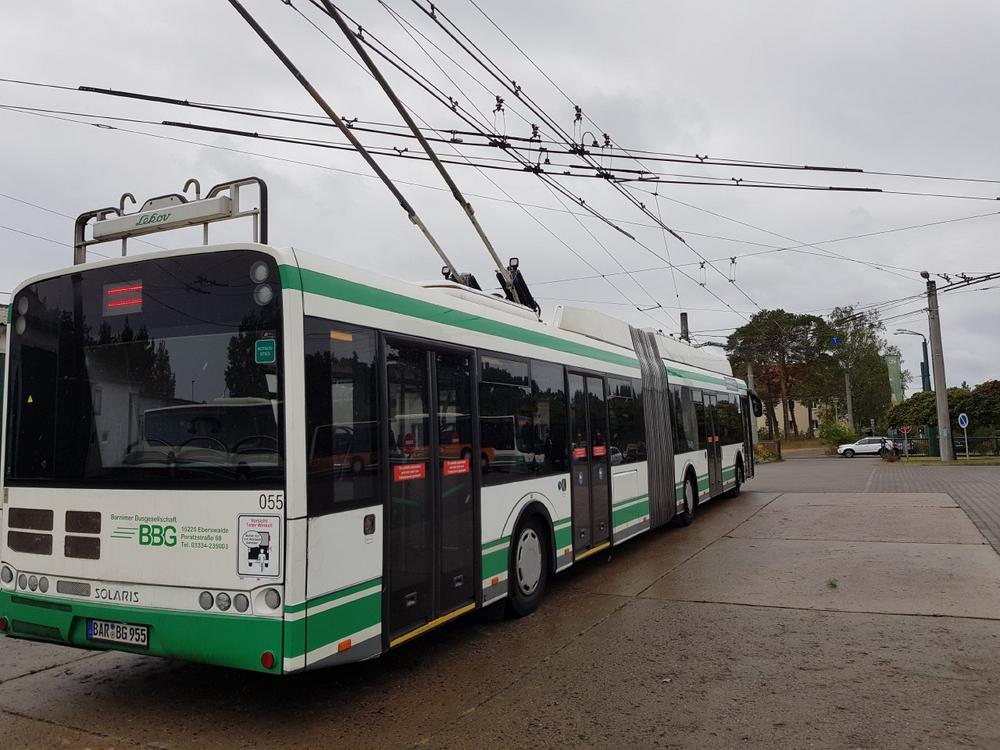
In-Motion-Charging for emission-free public transport
Moreover, additional operational freedoms can be used: relocation of circuits, extension of existing lines and expansion through new lines.
In April 2018, implementation of the hybrid trolleybuses began in the four project cities Eberswalde (DE), Szeged (HU), Gdynia (PL) and Arnhem (NL). So far, it has been shown that the expansion with in-motion charging technology pays off, especially in cities with a historic old town centre. In historical areas, the installation of the overhead line system can be omitted.
Since the start of the project there have been various unforeseen challenges, including the COVID 19 pandemic, but trolley:2.0 is still largely on schedule and will be completed as planned at the end of 2020.
New findings on the possibilities of battery electric trolley buses and smart trolley networks in the four partner cities
After the last interim report from 2019, the trolley:2.0 project and the partner cities have again seen many developments. Last year, for example, all cities invested in several hybrid trolleybuses that are already in use on some routes. Through power supply from both the overhead lines and the on-board batteries has particularly improved service in the outskirts of the partner cities.
In Arnhem, the trolleybuses can operate autonomously for at least ten kilometres, thus ensuring local zero-emission public transport also outside of the city. In the future, it is planned that only battery-electric trolleybuses will be used throughout Arnhem’s city transport system. The sections without overhead contact line will be battery electric.
Completely local emission-free travel is now also possible in the Eberswalde’s city area, after BBG Eberswalde has converted its buses with lithium-ion batteries. BBG is planning the complete conversion of the currently diesel-powered regional bus line and intends to operate it as a battery electric trolleybus line.
To date, nine of the 12 trolleybuses have already been equipped with batteries for this purpose. From September 2020, the first battery-powered trolleybuses will operate on line 910.
Just as Arnhem and Eberswalde, the Polish city of Gdynia is working on expanding trolleybus lines throughout the metropolitan region. On the one hand, the plans focus on existing routes on which diesel buses are to be replaced by trolley and electric buses. On the other hand, the transport companies are also developing new trolleybus lines, which are to run on parts of the route without overhead lines.
In Szeged, Hungary, the economic efficiency of the systems will be increased by the development and preparation for the use of new midi trolleybus types (8m) based on batteries. The first midi-battery trolleybus was built in April 2020 and has already undergone several tests. Eventually it will operate on the 77A line in Szeged, where it will run for 30 km with up to 20 km without overhead line. The bus will benefit from a weight reduction of 20 percent owed to the composite frame, which also acts as an insulating material.
Challenges in the project process
There were delays in certain project steps in all four cities. Frequent causes were lack of certification of the vehicles, which took longer than planned, or technical problems with the batteries. In Eberswalde, for example, new technical hurdles such as the software compatibility of battery and bus regularly arose and repeatedly presented new challenges for BBG and battery manufacturers. For BBG Eberswalde, this meant that the conversion of the trolleybuses was enormously delayed due to the greater time required for battery procurement and installation. The new plan is therefore that the first battery trolleybuses will operate on line 910 from September 2020.
The spread of the coronavirus has created additional challenges in the partner cities, as travel restrictions have prevented technicians from reaching the cities and delayed deliveries.
Study on SES systems in Gdynia
Due to the continuous exchange of information between the public transport companies and the respective project universities of Dresden, Gdynia, Delft and Gdansk, studies are always pending within the framework of trolley:2.0 to support the success of the project. In Gdynia, for example, a study was conducted on the possibilities of Stationary Energy Storage (SES) systems including the use of 2nd life batteries. A rectifier substation was equipped with an SES system to store recuperated energy. At the same time, power peaks from the upstream energy supply were reduced during energy withdrawal. This also reduced the cost component of 15 minutes of power supply and at the same time improved voltage stability in the catenary system.
Plans for the construction of a 350kW opportunity charger in Arnhem
The consortium partner Power Research Electronics is also currently developing a DC charger prototype, which will subsequently be tested integrated into the trolley networks in Eberswalde and Arnhem. This should enable hybrid trolleybuses to charge the battery for a few minutes at terminus stations and ensure safe circulation. The design should be ready by August and then tested. The final evaluation of the system is planned for December 2020 at the latest.
Electric Mobility Europe project trolley:2.0 promotes acceptance of hybrid trolleybuses
In the two years since the project started, the trolley:2.0 project supported by Electric Mobility Europe (EME) has helped to create a better basis for the evaluation of hybrid trolleybuses. The User Forum Meetings, which took place in Solingen in November 2018 and in Linz one year later, have improved the acceptance of trolleybuses in Europe, which are intended to make transport in cities locally emission-free.
A total of around 200 participants took part in the trolley:2.0 User Forum and used the opportunity to exchange views on trolley:2.0 innovations, on the latest developments in hybrid trolleybuses, and on smart trolley networks. Numerous feasibility studies for the installation of hybrid trolleybus lines could be prepared and carried out with the help of the trolley:2.0 user forum.
"Hereby, the trolley:2.0 project contributes to the current renaissance of trolleybus systems in Europe."
Eine moderne Stadtentwicklung und die Sicherung der städtischen Mobilität sind heute zwei wichtige Herausforderungen, um die Lebensqualität im urbanen Raum nachhaltig zu erhalten. Intelligente und moderne öffentliche Verkehrssysteme gewährleisten das fundamentale Recht auf Mobilität bei gleichzeitiger Minimierung negativer Umwelteinflüsse wie Schadstoffe, Lärm oder den Verbrauch von städtischen Lebensräumen.
Das Trolleybus-System ist eine erprobte und zukunftsfähige elektrische Antriebstechnologie zur Bewältigung dieser Herausforderungen. Es bietet dieselben Vorteile für die Stadtentwicklung wie die an Schienen gebundenen Systeme U-Bahn und Straßenbahn, kann jedoch deutlich rascher und flexibler auf das Wachstum von Städten reagieren.
trolley:motion wurde 2004 gegründet und ist seit 2007 als gemeinnütziger Verein eingetragen, der sich international für die Erhaltung, den Auf- und Ausbau von elektrischen Stadtbus-Systemen sowie für die Weiterentwicklung des Trolleybus-Systems engagiert.
trolley:motion: unsere Hauptaufgaben
Information und Aufklärung über zukunftsfähige städtische Mobilitätslösungen, insbesondere Trolleybus- Systeme (Website, Fachwiki, …)
Organisation internationaler Fachkonferenzen: Zürich 2008, Luzern 2010, Leipzig, 2012, Hamburg 2014 und Berlin 2016
Mitarbeit in (EU-)Forschungsprojekten (u. a. ACTUATE, ELIPTIC, TROLLEY, trolley:2.0) und die Koordination von Experten
Erfahrungsaustausch und Vernetzung von Städten und Unternehmen
Wissenstransfer zwischen Entscheidungsträgern, Mitarbeiter von Verkehrsbetrieben und Interessierte
Öffentlichkeits- und Lobbyingarbeit für den Trolleybus
trolley:motion, Verein z. Förderung von modernen E-Bus-Systemen
Ladaustraße 73
A5321 Koppl
Telefon: +43 (664) 4141866
http://www.trolleymotion.eu
Präsident
E-Mail: backhaus@trolleymotion.eu
Presse, Marketing
Telefon: +43 (664) 4141866
E-Mail: scharzenberger@trolleymotion.eu
![]()